
High-Pressure Laser Floating Zone Furnace
Floating zone is a crucible-free crystal growth method where an optical heating source melts a small portion of a polycrystalline sample, suspending the melt via surface tension alone. Subsequent translation of the sample leads to directional crystallization, allowing for the generation of high-quality, large-volume single crystals particularly suitable for weakly interacting probes such as neutron scattering.
The high-pressure furnace design at Rice features seven 200 W fiber lasers and an all-metal growth chamber enabling crystal growth under applied gas pressures up to 1,000 atm. This pressure range offers users a powerful tuning knob to control disorder, material volatility, and chemical potential during recrystallization. Available gas environments are UHP Ar, UHP N2, and an 80:20 Ar:O2 gas blend. A camera and pyrometer allow for live viewing and temperature monitoring during growth. The high-power fiber lasers have a tunable incident spot size, allowing for precise control over the temperature gradient at the hot zone.
Image captions:
1: “High-Pressure Laser Floating Zone Furnace”
2: “Floating zone crystal growth under 70 atm”

Quantum Design 9T Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS) DynaCool
The PPMS performs electrical and thermal transport, heat capacity, and magnetization measurements at temperatures down to 1.8 K and at magnetic fields up to ±9 T. Additional capabilities include high-voltage in-situ uniaxial strain measurements based on piezostack techniques with external lock-in amplifiers.
Image caption:
“Quantum Design 9T Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS) DynaCool”

Laue X-ray Diffractometer
Used for orienting single crystal samples, the Laue diffractometer uses a backscattered, white beam of X-rays to generate a diffraction pattern from the sample surface. This tool is equipped with a motorized goniometer for precision control of crystal orientation.
Image Caption:
“Laue X-ray Diffractometer”

High-Temperature Furnaces
Box furnaces and tube furnaces are available for solid-state reactions, flux-based crystal growth, and preparation of polycrystalline feed rods for floating zone growth. Tube adapters enable vacuum operation or gas flow for inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments during heating.
Image caption:
“High-temperature box furnaces and tube furnaces”

Bruker D8 Advance x-ray Diffractometer (XRD)
With low temperature stage: can be used for a variety of materials characterization and analysis applications, such as identifying the crystal structure and composition of single and polycrystalline samples. It can operate at liquid nitrogen temperatures (using a closed-cycle cryostat), which allows for the investigation of materials that exhibit changes in their crystal structure or properties at low temperatures.
Image caption:
"Bruker D8 Advance x-ray Diffractometer (XRD)"
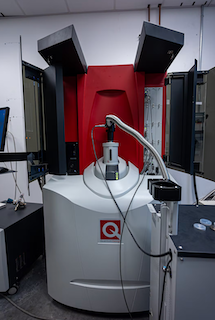
Cryogen-free Quantum Design MPMS3 SQUID magnetometer with He3
With excellent sensitivity (down to 10-9emu) for different types of AC and DC magnetic measurements with a wide temperature range T = 0.4 K to 400 K and maximum magnetic fields of up to 7 T.
Image caption:
“Cryogen-free Quantum Design MPMS3 SQUID magnetometer with He3”

Cryogen-free Quantum Design Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS) DynaCool
For studying magnetic, thermal, and transport properties of materials in a wide temperature range (50 mK to 400 K) and magnetic fields up to 14 T. The PPMS DynaCool system is equipped with a range of measurement capabilities, including AC susceptibility, DC magnetometry, resistivity, and heat capacity.
Image caption:
“Cryogen-free Quantum Design Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS) DynaCool”

Single-arc furnace
Used for fast-melting of intermetallic plycrystalline alloys, and sealing growths in vacuum metal tubes
Image caption:
“Single-arc furnace”
